RAEGE Network
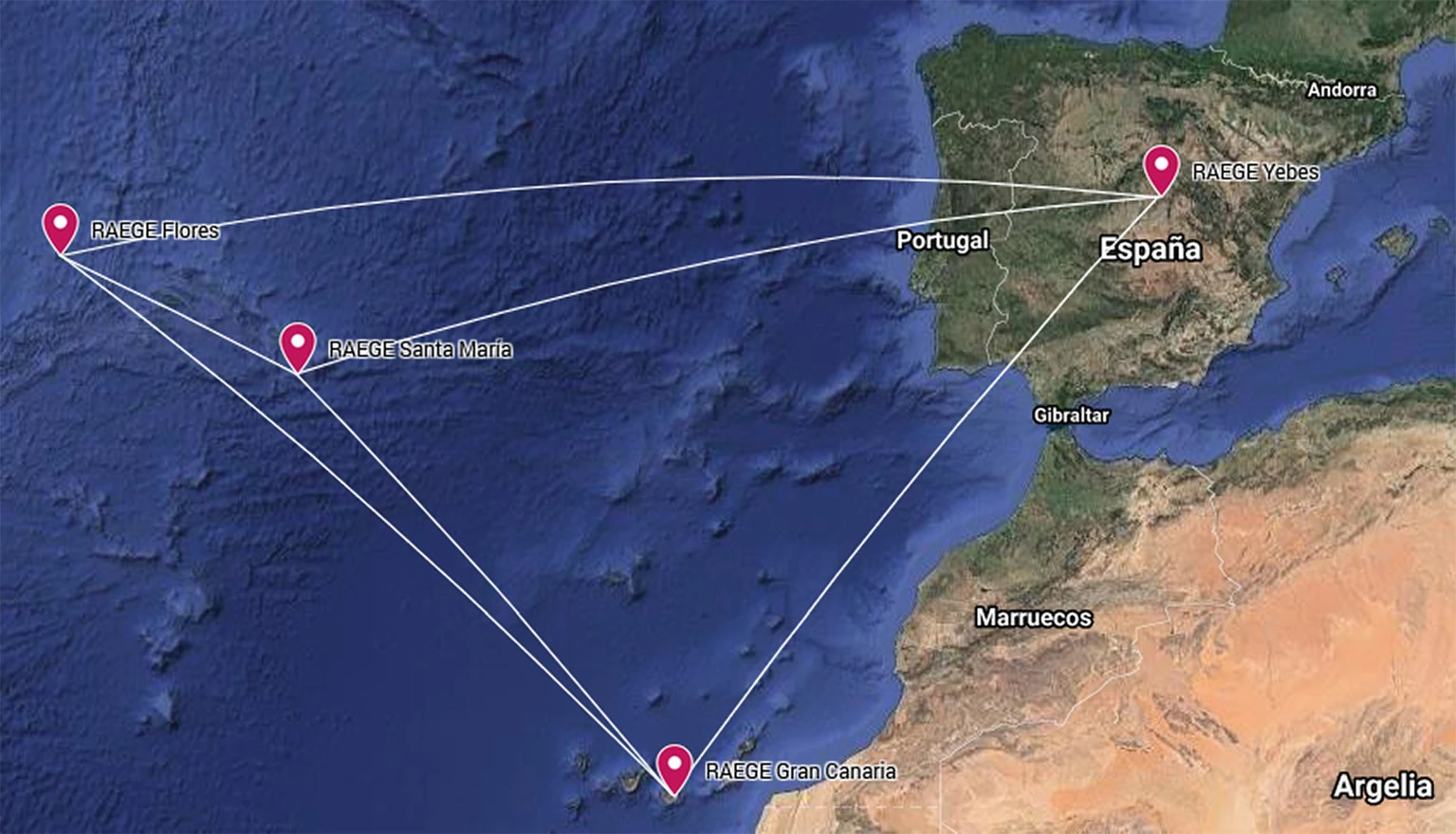
Designada por Rede Atlântica de Estações Geodinâmicas e Espaciais, o projeto RAEGE começou em 2010 com a assinatura de um memorando de entendimento entre o Governo de Espanha e o Governo dos Açores, para a construção, instalação e exploração de quatro Estações Geodésicas Fundamentais: duas em Espanha (Yebes e Gran Canária) e duas nos Açores (Santa Maria e Flores).
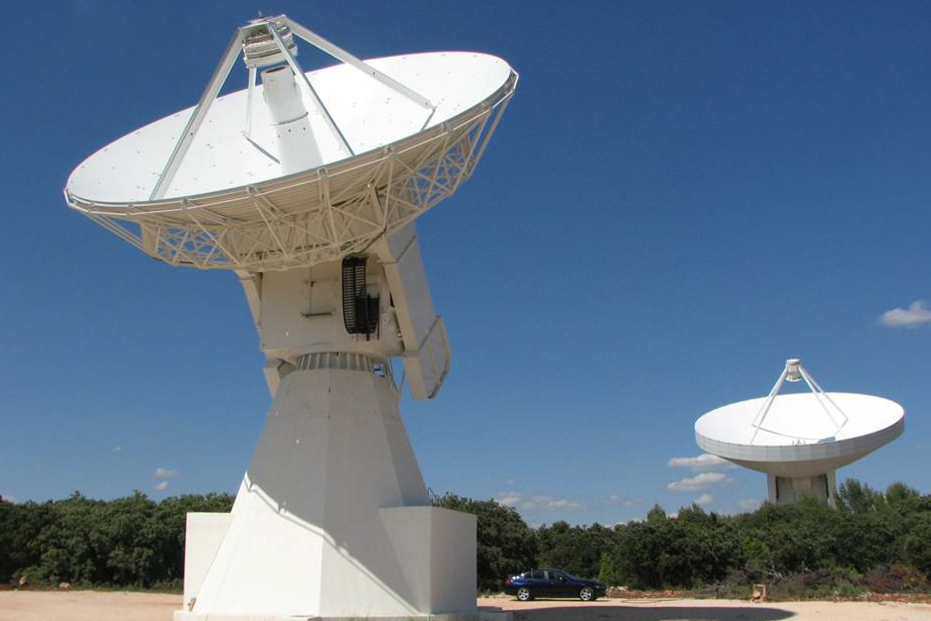

All this equipment provides a geodetic infrastructure necessary for monitoring the Earth’s surface capable of providing high-precision data to the scientific community, allowing the quantification of changes in space and time of our planet. The observations make it possible to map and monitor changes in Earth’s shape, rotation, and mass distribution, contributing to the updating of the international terrestrial references (ITRF) and thus being able to study relevant issues such as those who are associated with climate change, estimates the average variation of sea level, etc.
RAEGE stations are also strategically located on different tectonic plates: the Eurasian plate (Yebes, Spain), the North plate (Flores, Azores), the African plate (Gran Canaria, Spain), and on the micro-plate, the triple junction of Azores (Santa Maria, Azores).
RAEGE contributes to the GGOS (Global Geodetic Observing System) of the International Geodetic Association (IGA) through several international networks where it is inserted. The main objective of GGOS is the updating, expansion, and maintenance of a global network of Fundamental Geodetic Stations, which provide data to a better understanding of the dynamics of the Earth’s environment and the consequences of climate changes on our planet for decision making regarding the long-term social impact.
RAEGE’s strategic objectives are:
- Full integration of RAEGE radiotelescopes into VGOS network;
- Conclusion of four GGOS Stations;
- Enhancement, integration, and increment of activities in partnership with other scientific entities such as universities, science centres, collaborative laboratories, and/or science networks.